|
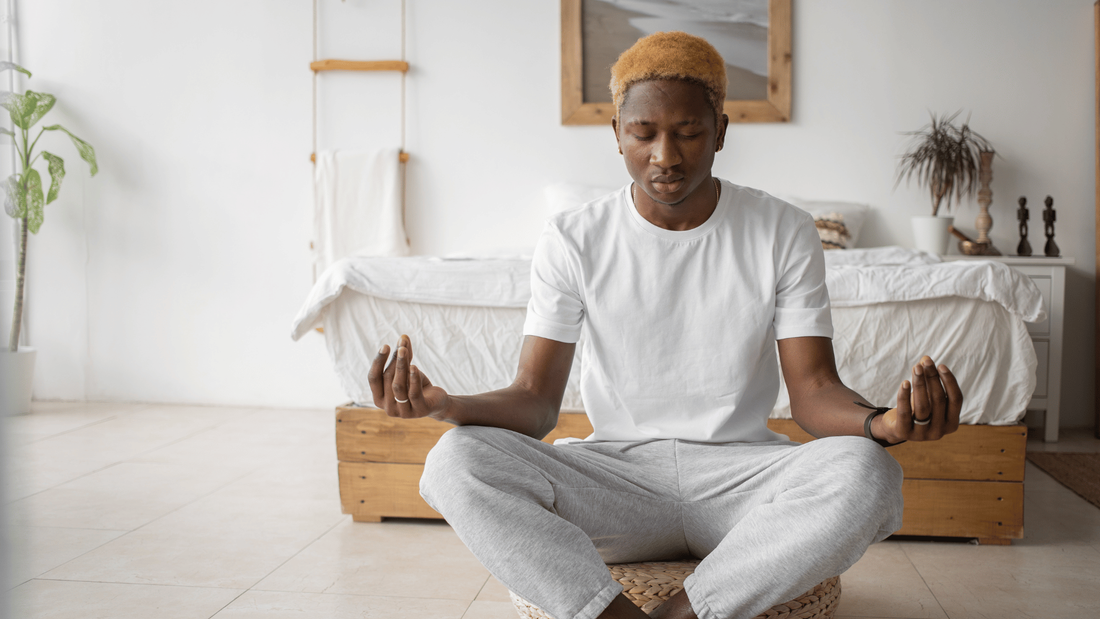
Science has now caught up to why mindfulness meditation has been around for thousands of years.
Mindfulness is an ancient practice of focusing on the present moment with kind awareness. Other modalities such as meditation and yoga are practices that help you develop your awareness to the present moment. Keep reading to discover 10 science-backed psychological and physical benefits of mindfulness meditation. Mindfulness has been shown to:1. Improves attention, focus, and learning outcomes
A study found that people who meditated showed improved attention and accuracy while completing tasks compared to those in a control group. (11)
Another study assigned participants to listen to four sessions of a recorded meditation training or an audio book recording. Both interventions were effective at improving mood but only the meditation training reduced fatigue, anxiety, and significantly improved visual-spatial processing, working memory, and executive functioning. (3) 2. Increases ability to self-regulate emotions and behaviors
Mindfulness helps individuals become aware of the emotions and engage with them in a different and more productive way.
A review of studies concluded that mindfulness supports various positive psychological effects such as improved behavioral regulation. (4) 3. Decreases work related stress and burn-out while increasing focus and efficacy in doing your job
Participation in a mindfulness-based professional development program resulted in significant improvements in teacher well-being, efficacy, and burnout/time-related stress, compared to teachers in a control group. (1)
4. Reduces feelings of anxiety and stress Reduces anxiety
In a randomized controlled trial, Mindful Based Stress Reduction Training was associated with a significant reduction in anxiety in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. (7)
Additionally, Johns Hopkins University analyzed 47 trials with over 3,500 people. They concluded that mindfulness meditation programs can help improve anxiety. (15) 5. Reduces Implicit Age and Race Bias
A study had participants listen to either a mindfulness recording or a controlled audio and then complete a race and age implicit association test (IATs).
The group who listened to the mindfulness recording showed a significant decrease in implicit race and age bias when compared to the control group. (8) 6. Helps prevent depression from reoccurring
A study compared mindfulness training to antidepressants in the recurrence of depression between 2 groups of patients.
They found no difference in recurrence of depression between either groups suggesting that mindfulness training was as effective as antidepressants in helping to prevent depression recurrence. (9) 7. Reduce Inflammation
In an 8-week study, a meditation style called “mindfulness meditation” reduced the inflammatory response caused by stress. (12)
8. Enhances memory
One study found that meditating for just 13 minutes daily enhanced attention and memory after 8 weeks. (13)
9. May help your sleep better
Researchers found that people who meditated stayed asleep longer and had less severe symptoms of insomnia, compared with those who had an unmedicated control condition. (14)
10. Helps regulate HR and blood pressure
A meta-analysis of 12 studies enrolling nearly 1000 participants found that meditation helped reduce blood pressure. (5)
This was more effective among older volunteers and those who had higher blood pressure prior to the study
Mindfulness helps you become more intentional about how you live your life. It not only improves memory, executive functioning skills, and your ability to focus but also it has immense physiological benefits such as decreasing inflammation in your body, lowering blood pressure and getting a better night's sleep.
Ready to start your mindfulness practice? Join our FREE 7 Day Mindfulness Challenge. Join the FREE 7 Day Mindfulness ChallengeThank you!Please check your email to access content. References: 1. Flock, L., Goldber, S.B., Pinger, L., Bonus, K., & Davidson, R.J. (2013). Improving Classroom Learning Environment by Cultivating Awareness and Resilience in Education (CARE): Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. School Psychology Quarterly, 28(4), 374-390. 2. Roeser, R., Schonert-Reichl, K.A. Jha, A., Cullen, M., Wallace L., Wilensky, Harrison, J. (2013) Mindfulness training and reductions in teacher stress and burnout: Results from two randomized, waitlist-control field trials. Journal of Education Psychology, 105(3), 787-804. 3. Zeidan, F., et al. Mindfulness meditation improves cognition: Evidence of brief mental training. Consciousness and Cognition (2010), doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2010.03.014 Keng SL, Smoski MJ, Robins CJ. Effects of mindfulness on psychological health: a review of empirical studies. Clin Psychol Rev. 2011 Aug;31(6):1041-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.04.006. Epub 2011 May 13. PMID: 21802619; PMCID: PMC3679190. 4. Bai Z, Chang J, Chen C, Li P, Yang K, Chi I. Investigating the effect of transcendental meditation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hum Hypertens. 2015 Nov;29(11):653-62. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2015.6. Epub 2015 Feb 12. PMID: 25673114 5. Barnes, V.A., Davis H. C., Murzynowski, J.B., & Treiber, F.A. (2004). Impact of meditation on resting and ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate in youth. Psychosomatic Medicine, 66(6), 909-914. 6. Hoge EA, Bui E, Marques L, Metcalf CA, Morris LK, Robinaugh DJ, Worthington JJ, Pollack MH, Simon NM. Randomized controlled trial of mindfulness meditation for generalized anxiety disorder: effects on anxiety and stress reactivity. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013 Aug;74(8):786-92. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m08083. PMID: 23541163; PMCID: PMC3772979. 7. Lueke A, Gibson B. Mindfulness Meditation Reduces Implicit Age and Race Bias: The Role of Reduced Automaticity of Responding. Social Psychological and Personality Science. 2015;6(3):284-291. doi:10.1177/1948550614559651 8. Kuyken W, Hayes R, Barrett B, Byng R, Dalgleish T, Kessler D, Lewis G, Watkins E, Brejcha C, Cardy J, Causley A, Cowderoy S, Evans A, Gradinger F, Kaur S, Lanham P, Morant N, Richards J, Shah P, Sutton H, Vicary R, Weaver A, Wilks J, Williams M, Taylor RS, Byford S. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy compared with maintenance antidepressant treatment in the prevention of depressive relapse or recurrence (PREVENT): a randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2015 Jul 4;386(9988):63-73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62222-4. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Erratum for: Lancet. 2016 Oct 1;388(10052):1376. PMID: 25907157. 9. Albertson, E.R., Neff, K.D. & Dill-Shackleford, K.E. Self-Compassion and Body Dissatisfaction in Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial of a Brief Meditation Intervention. Mindfulness 6, 444–454 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-014-0277-3 10. Norris CJ, Creem D, Hendler R, Kober H. Brief Mindfulness Meditation Improves Attention in Novices: Evidence From ERPs and Moderation by Neuroticism. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018 Aug 6;12:315. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00315. Erratum in: Front Hum Neurosci. 2018 Sep 05;12:342. PMID: 30127731; PMCID: PMC6088366. 11, Rosenkranz MA, Davidson RJ, Maccoon DG, Sheridan JF, Kalin NH, Lutz A. A comparison of mindfulness-based stress reduction and an active control in modulation of neurogenic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2013 Jan;27(1):174-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Oct 22. PMID: 23092711; PMCID: PMC3518553. 12. Basso JC, McHale A, Ende V, Oberlin DJ, Suzuki WA. Brief, daily meditation enhances attention, memory, mood, and emotional regulation in non-experienced meditators. Behav Brain Res. 2019 Jan 1;356:208-220. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.08.023. Epub 2018 Aug 25. PMID: 30153464. 13. Ong JC, Manber R, Segal Z, Xia Y, Shapiro S, Wyatt JK. A randomized controlled trial of mindfulness meditation for chronic insomnia. Sleep. 2014 Sep 1;37(9):1553-63. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4010. PMID: 25142566; PMCID: PMC4153063. 14. Goyal M, Singh S, Sibinga EMS, et al. Meditation Programs for Psychological Stress and Well-being: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(3):357–368. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.13018 15. Hoge EA, Bui E, Marques L, Metcalf CA, Morris LK, Robinaugh DJ, Worthington JJ, Pollack MH, Simon NM. Randomized controlled trial of mindfulness meditation for generalized anxiety disorder: effects on anxiety and stress reactivity. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013 Aug;74(8):786-92. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m08083. PMID: 23541163; PMCID: PMC3772979.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Hi, I'm AlyssaMindfulness, yoga, and herbal medicine have been fundamental to my own journey in life. I hope to share my experiences and perspectives in order to inspire and connect with others. Archives
January 2024
Categories
All
|
|
Herbs Love And Yoga
111 Church Hill Rd., Suite 1 Sandy Hook, CT 06482 |
(917) 267-8203
[email protected] |
Proudly powered by Weebly


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

